Special Feature : Delivering to the world the material of possibilities - TUNGSTEN Vol.2
To Strengthen Resource Circulation
Tungsten is a material that is full of potential. With the evolution of generative AI, xEVs, and various other technologies, its demand is expected to increase going forward. In order to continue to support the evolution of technology, it is necessary to prevent the risk of being unable to procure tungsten. The trump card for this is resource circulation for tungsten. Aiming to become a leading company in tungsten products recognized by customers globally, Mitsubishi Materials will consolidate the Group’s capabilities and further enhance resource circulation efforts to handle all aspects of the world’s tungsten recycling.
Group companies responsible for tungsten recycling together with Mitsubishi Materials
Mitsubishi Materials Europe B.V.
Was established in Amsterdam, the Netherlands in September 2024. The company will formulate and implement strategies in Europe, including the E-Scrap recycling business and the tungsten business. Its role will also include managing and supervising operating companies in Europe and managing copper mine dividends. Its main business activities are the recycling design, mineral resources, and tungsten businesses.
Was established in Amsterdam, the Netherlands in September 2024. The company will formulate and implement strategies in Europe, including the E-Scrap recycling business and the tungsten business. Its role will also include managing and supervising operating companies in Europe and managing copper mine dividends. Its main business activities are the recycling design, mineral resources, and tungsten businesses.

H.C.Starck Holding (Germany) GmbH
H.C. Starck is a world-leading tungsten product manufacturer with over 100 years of history that possesses worldclass tungsten recycling capabilities. It has its head office and plant in Germany and manufactures and sells high-quality powders made mainly of tungsten, tungsten carbide, and its alloys. It manufactures and sells products in Europe, North America, and China, and Japan is included in its sales network.
H.C. Starck is a world-leading tungsten product manufacturer with over 100 years of history that possesses worldclass tungsten recycling capabilities. It has its head office and plant in Germany and manufactures and sells high-quality powders made mainly of tungsten, tungsten carbide, and its alloys. It manufactures and sells products in Europe, North America, and China, and Japan is included in its sales network.

Japan New Metals Co., Ltd.
This is the only company in Japan with tungsten refining technologies, capable of producing tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder from tungsten-containing scrap through an integrated process. By leveraging its strength in hydrometallurgy technology to reuse scrap, it aims to advance resource circulation in Japan and establish a system for a resource-recycling society.
This is the only company in Japan with tungsten refining technologies, capable of producing tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder from tungsten-containing scrap through an integrated process. By leveraging its strength in hydrometallurgy technology to reuse scrap, it aims to advance resource circulation in Japan and establish a system for a resource-recycling society.

Benefits of the H.C. Starck and Japan New Metals collaboration
・Strengthening R&D capabilities through joint development
・Creating synergy and enhancing corporate value through promotion of cross-selling, etc.
・Strengthening R&D capabilities through joint development
・Creating synergy and enhancing corporate value through promotion of cross-selling, etc.
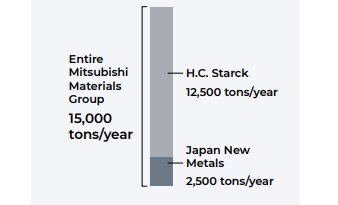
Sixfold growth in supply capacity
The current tungsten supply capacity of Japan New Metals is 2,500 tons per year. Meanwhile, H.C. Starck’s supply capacity across its European, North American, and Chinese production bases is 12,500 tons per year. Following the acquisition of H.C. Starck, the entire Mitsubishi Materials Group now has a world-class supply capacity of 15,000 tons per year, increasing its previous supply capacity sixfold. The Group
will strengthen its tungsten business foundation and further accelerate the advancement of its business strategy.
will strengthen its tungsten business foundation and further accelerate the advancement of its business strategy.

Tungsten powder
Expansion of scrap collection volume
Our Group is increasing the volume of tungsten scrap collected, such as used carbide tools, both in Japan and abroad. The primary collection method involves gathering used tools from customers through the carbide tool sales network. There are also cases in which we purchase scrap from scrap dealers. Additionally, we are considering collaboration with E-Scrap collection efforts, which is being carried out by Mitsubishi Materials’ Metals Company. This would involve jointly collecting E-Scrap and tungsten carbide scrap generated in Europe, and then delivering E-Scrap to copper smelters and refineries in Japan and tungsten carbide scrap to H.C. Starck, thereby increasing the scrap collection volume.

Carbide tools (cutting tools, etc.)

Tungsten carbide scrap (used carbide tools)
World-class recycling capacity
Combining Japan New Metals and the German bases of H.C. Starck, we can secure one of the largest recycling capacities in the world. H.C. Starck and Japan New Metals are both planning to further increase recycling capacity toward 2030. Through these efforts, Mitsubishi Materials Group is aiming for a recycled raw material ratio of 80% or more for the manufacture of carbide tools by 2030.

Intermediate powder

Tungsten carbide powder
Expansion of global sales channels
By utilizing and combining Japan New Metals’ highly functional powders and H.C. Starck’s sales network, we will expand sales channels to various areas of the world, such as Europe, the United States, and China. This will meet the demands of industries worldwide, not only by supporting state-of-the-art manufacturing with carbide tools but also by providing powders for various applications, such as a material for rechargeable batteries. We will also advance recycling of used tungsten through collection.
POINT
What proprietary technology is used for tungsten refining?
At the Akita Plant of Japan New Metals, collected scrap goes through a method of processing called oxidation roasting and is turned into powder. Using the only hydrometallurgy technology in Japan, this powder is made into APT (ammonium paratungstate), an intermediate product. Following this, in the dry processing process, APT goes through calcination, deoxidization, and carbonization processing to manufacture tungsten carbide powder.
Tungsten processing methods vary by region, depending on local infrastructure and the specific composition requested by customers. The strength of Japan New Metals’ processing technologies lies in its lineup, which is capable of responding to these global trends. On the other hand, H.C. Starck carries out recycling using the world’s only hydrometallurgy technology that uses solvent extraction. We aim to enhance our refining capabilities by integrating the technologies of both companies.
What proprietary technology is used for tungsten refining?
At the Akita Plant of Japan New Metals, collected scrap goes through a method of processing called oxidation roasting and is turned into powder. Using the only hydrometallurgy technology in Japan, this powder is made into APT (ammonium paratungstate), an intermediate product. Following this, in the dry processing process, APT goes through calcination, deoxidization, and carbonization processing to manufacture tungsten carbide powder.
Tungsten processing methods vary by region, depending on local infrastructure and the specific composition requested by customers. The strength of Japan New Metals’ processing technologies lies in its lineup, which is capable of responding to these global trends. On the other hand, H.C. Starck carries out recycling using the world’s only hydrometallurgy technology that uses solvent extraction. We aim to enhance our refining capabilities by integrating the technologies of both companies.











